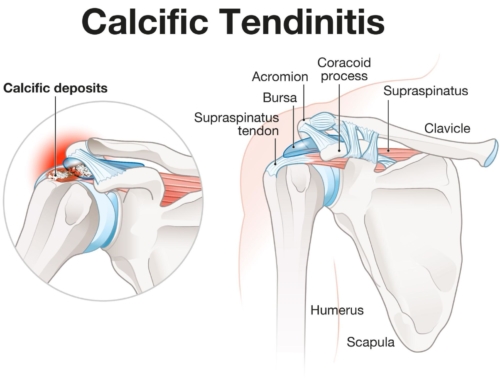
1. What is calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder?
Calcific tendinopathy of the rotator cuff (deep muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint) is a common condition with a reported incidence rate of 2.5-7.5% (Chianca et al, (2018). Research has demonstrated that between 10 to 20% calcific tendinopathy patients have evidence of calcification on both shoulders. A majority of calcific masses (80%) are located in the supraspinatus tendon, 15% in the infraspinatus tendon and 5% in the subscapularis tendon (see below image). The development of a calcific shoulder tendinopathy commonly occurs within the 4th and 5th decade of life and effects women (70%) more than men (30%).
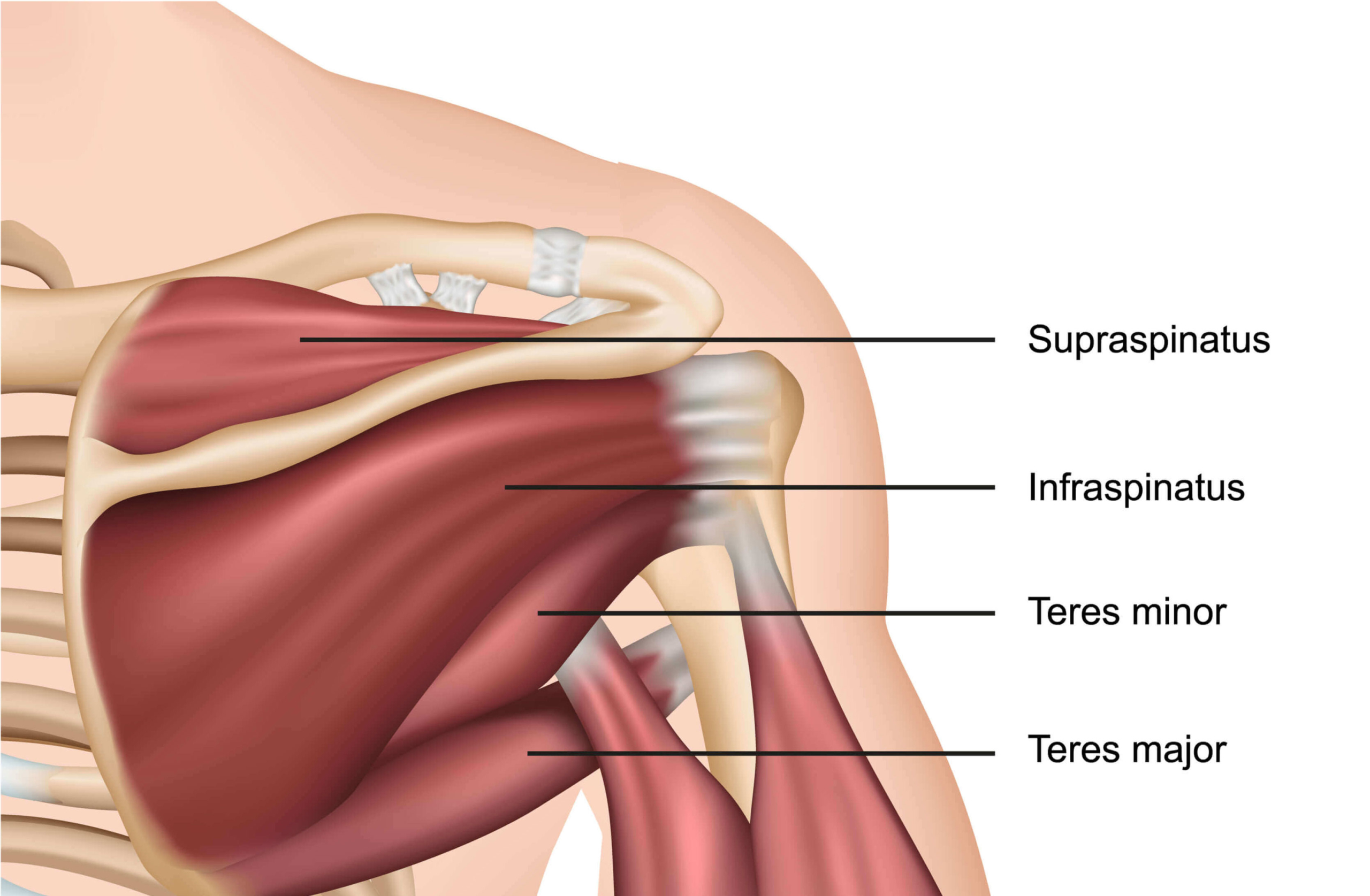
2. What causes calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder?
The underlying cause of calcific tendinopathy is not known however, it is believed to be instigated by the transformation of cells called tenocytes (used in the production of tendon tissue) into chondrocyte cells (used in the production of cartilage). This conversion is thought to initiate the production of calcium (bone) within the tendon structure (Chianca et al, 2018).
4. How do we treat calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder?
There are two evidence-based treatment options available to you to treat your calcific tendinopathy. We normally advise the least invasive treatment first; shockwave therapy, but this will depend on your specific situation. The pros and cons of both treatment options will be discussed with you.
- Shockwave therapy – shockwave is a non-invasive approach to the management of calcific tendinopathy pain and will be discussed in more detail within this blog.
- Ultrasound guided steroid injection/barbotage and lavage – this is an injection technique carried out under ultrasound guidance designed to breakdown and aspirate (‘suck out’) the calcium deposits. For more information about the barbotage and lavage procedure click here.
The classic presentation of calcific tendinopathy is rapid onset of severe pain for no apparent reason or injury. It causes a significant reduction in your range of movement and limits your ability to carry out simple tasks such as dressing and undressing.
To diagnose calcific tendinopathy requires either an ultrasound or an MRI scan. Ultrasound is better than MRI at demonstrating calcification within the rotator cuff tendons. The scan will ascertain the size, shape and location of the calcific deposit. At Complete we carry out an ultrasound scan at no extra charge.
4. How does shockwave therapy work for calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder?
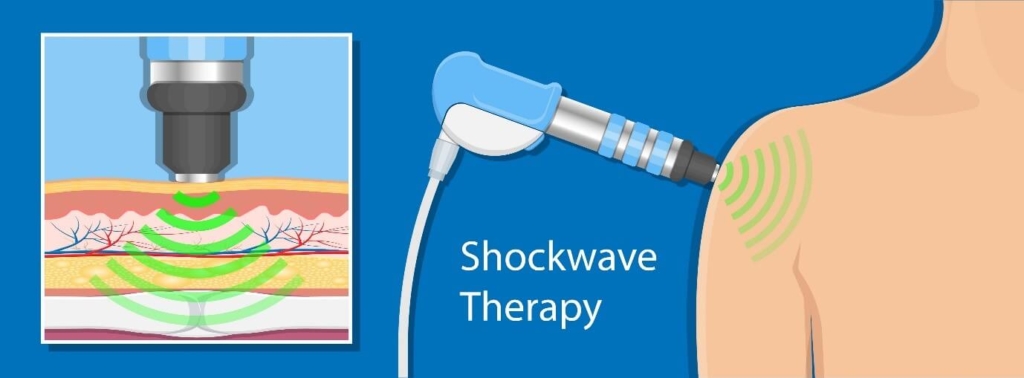
Shockwave therapy creates a series of potent sound waves which produces a small dose of controlled microtrauma direct to the calcific tendon. Research has shown that shockwave therapy stimulates the body’s natural healing process, induces fragmentation of calcium deposits within the tendon and desensitises local nerve endings, causing a reduction in pain and symptoms (Chianca et al., 2018).
5. Is shockwave therapy effective for calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder?
The use of shockwave therapy for calcific tendinopathy is well supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). NICE provides national guidance and advice to improve health and social care in the NHS. It provides evidence based recommendations to guide best practice within healthcare.

Shockwave therapy of calcific tendinopathy has been proven to be a clinically effective non-invasive treatment option for calcific tendinopathy. Schmitz et al (2015) conducted a systematic review to investigate the efficacy and safety of shockwave treatment for the treatment of orthopaedic conditions. Results of this extensive study reported shockwave to be a safe treatment technique for treating tendinopathy throughout the body. There has been no reported cases that shockwave treatment has caused any serious adverse effects.
Schmitz et al (2015) demonstrated that shockwave therapy is capable of significantly reducing pain and symptoms when compared to other treatment techniques for the rehabilitation of calcific tendinopathy. This systematic review observed 88.5% success rates, in relation to pain and increased function, when shockwave treatment was used. A further systematic review conducted by Huisstede et al (2011) also reflected these findings.
Research by Pakos et al (2018) observed increased benefits when ultrasound-guided injection techniques were used alongside shockwave treatment for treating calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder.
6. How many sessions and how often do you need shockwave therapy for calcific tendinopathy?
The current research base recommends the initial completion of three shockwave sessions spaced one week apart. This can be increased to 6 sessions if clinically appropriate and is dependent on the success of the initial shockwave treatments. Shockwave treatment can be uncomfortable however, research by Schmitz et al (2015) states that for effective outcomes the highest possible dose of shockwave tolerated by the patient should be applied.
Treatment parameters recommended within the research are as follows:
5. How long does it take to recover from calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder?
Recovery from calcific tendinopathy of the shoulder can vary between cases. It is not uncommon for patients to feel immediate relief following the first shockwave treatment however, most people find a progressive reduction in pain and symptoms during the treatment period. It is crucial that shockwave therapy be complimented with progressive rehabilitation program designed by physiotherapist.

6. Should you have an ultrasound scan before having shockwave therapy?
Gaining an accurate diagnosis is critically important, especially if calcific tendinopathy is suspected. Diagnostic ultrasound is highly effective and diagnosing the presence and location of calcific deposits within the rotator cuff tendons and therefore, ultrasound should be used to locate the position of the calcific deposit, allowing for a focused shockwave treatment.
If you suspect you have calcific tendinopathy and/or to find out whether shockwave therapy is an effective treatment option for you for you please ensure you book in with one of our expert physiotherapists to carry out an ultrasound scan. We do not charge extra for the ultrasound scan.
If you would like to book an appointment or would like more information before booking please call 020 7482 3875 or email info@complete-physio.co.uk
References:
Don’t let pain hold you back, book now!